
Uncovering the Mechanics of Timekeeping
A Guide To Watch Movements
Ever wondered what makes your watch tick—or stop ticking?—discover the fascinating world of watch movements and how they power everything from vintage heirlooms to modern smartwatches.

The Heart of Timepiece History
How Watch Movements Shaped the Story of Time
Watches have been a staple of human life since the 15th century. Over time, they’ve transformed from the ornate pocket watches of the 1600s into the sophisticated analog wristwatches of the 19th and 20th centuries, and today, many of us wear digital minicomputers on our wrists that do far more than just tell time. As the design and function of watches have evolved, so too have the internal systems that power them. These systems—known as movements—are the beating hearts behind every tick, turn, and complication.
This guide is dedicated to exploring those watch movements, diving into the history, mechanics, and character of each one. From the centuries-old elegance of mechanical timepieces to the unmatched precision of quartz and atomic watches, and the modern innovation of connected smartwatches, every type of movement offers something unique to horology lovers and casual wearers alike.
What Exactly Is a Watch Movement?
At the heart of each ticking watch is the system by which it powers all of its time-keeping functions: its movement.
A watch movement refers to the internal mechanism that drives all timekeeping functions. This includes the movement of the hands, the operation of complications like date indicators or chronographs, and in many modern cases, connectivity features like GPS or notifications. Without a functioning movement, a watch is essentially a bracelet—it may still look beautiful, but it has lost its soul.
The Types of Watch Movements
Traditionally, movements can be broken down into the following categories and subdivisions:
- Mechanical
- Manual Winding (aka Wind Up)
- Automatic (aka Kinetic/Self-Wind)
- Quartz
- Atomic
- Solar
- Connected
Movements are generally classified into three overarching types: mechanical, quartz, and connected. Mechanical movements can be further divided into manual and automatic subtypes. Quartz watches may include additional innovations such as atomic synchronization or solar charging. Connected watches represent the latest shift in wearable technology, where timekeeping is just one of many integrated features.

Mechanical Movements
The Craft of Mechanical Movements
Mechanical movements are the original method of powering a watch and remain highly respected for their complexity and artistry. These watches rely on a tightly wound mainspring that slowly unwinds, transferring energy through a series of gears that regulate the release of time in precise increments. No battery is required in a mechanical movement, which makes the process feel almost magical—completely powered by craftsmanship and physics. There are two types of mechanical movements.
Manual Winding Watch Movements
The first, manual winding watches, requires the wearer to wind the crown regularly in order to maintain power. This style of watchmaking dates back centuries and is cherished by collectors and connoisseurs who appreciate the tactile ritual and the historical continuity it offers. These watches are often found in antique collections or high-end pieces where traditional craftsmanship is prioritized.
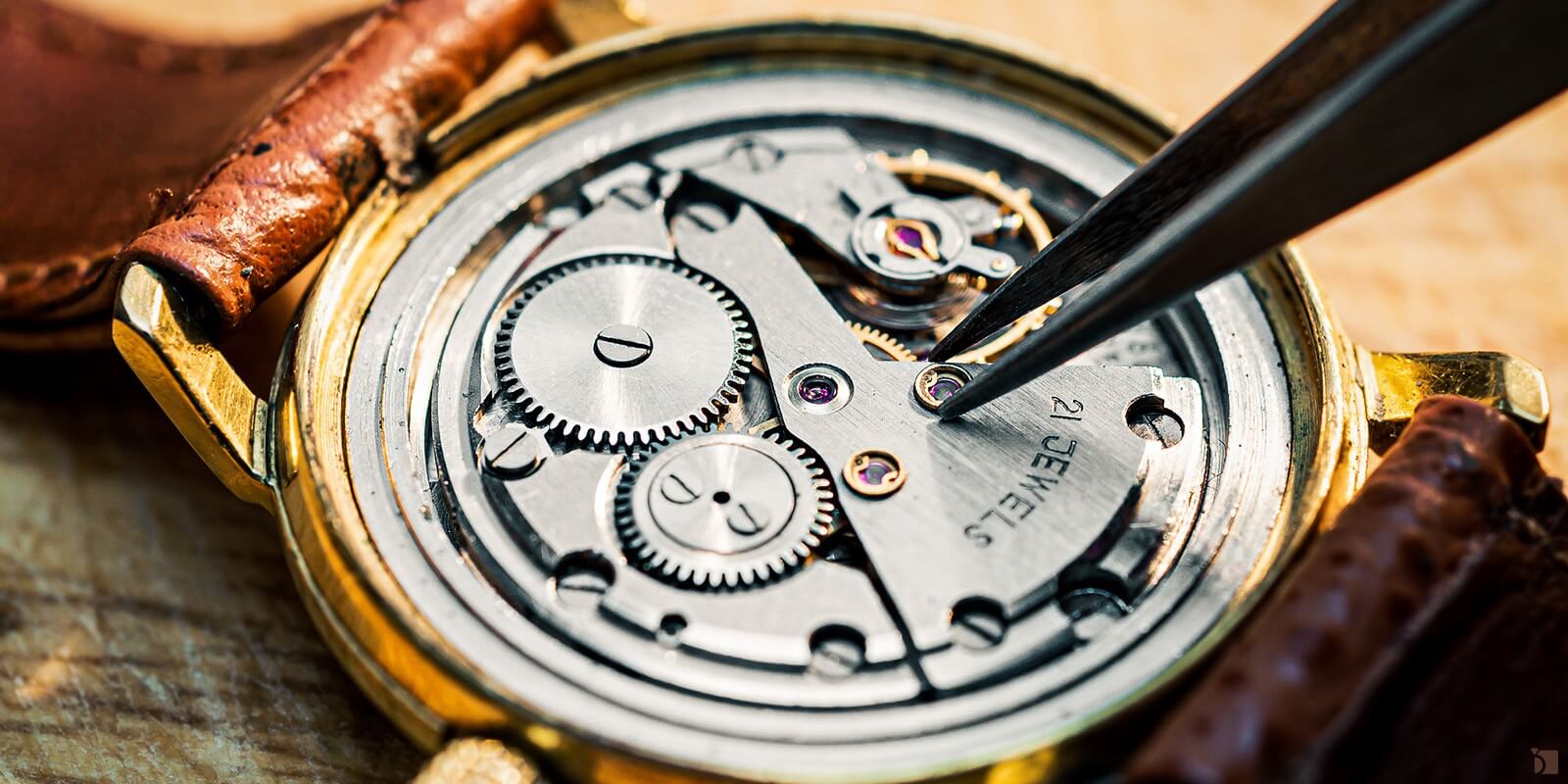

Automatic Watch Movements
The second type is the automatic movement. These watches operate on the same mechanical principle as manual ones but include an ingenious addition—a small weighted rotor that spins with the motion of the wearer’s wrist. As it spins, it winds the mainspring automatically, keeping the watch powered so long as it’s worn regularly. Automatic movements rose to popularity in the early 20th century and are particularly favored for their convenience and engineering brilliance. Dive watches, for instance, frequently use automatic movements due to their reliability and hands-free winding system. However, if the watch is left unworn for a period of time, it may stop and require a bit of manual assistance to restart.
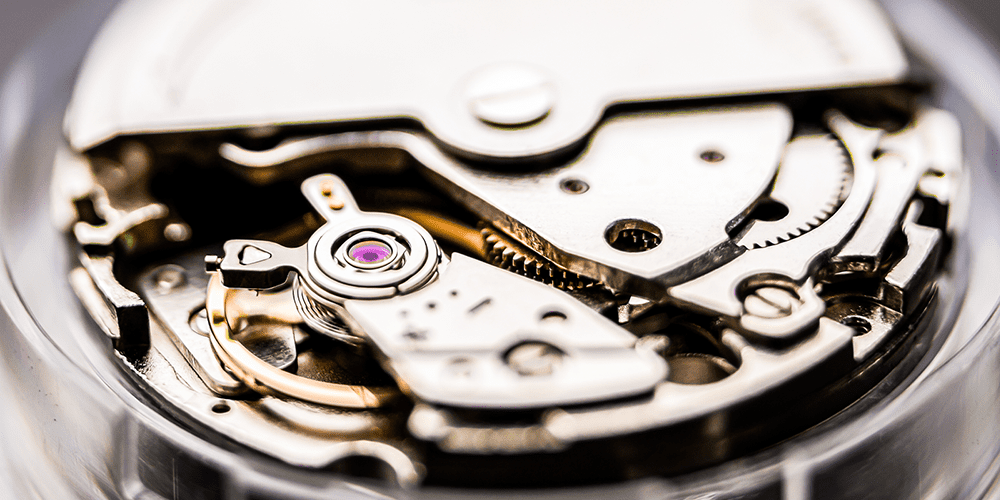
Brands Known For Extraordinary Mechanical Watches
Even in the face of newer technologies, mechanical movements remain central to high-end watchmaking. Brands such as Rolex, Patek Philippe, Audemars Piguet, and Vacheron Constantin have continued to craft extraordinary mechanical watches that represent the height of horological expertise. To enthusiasts, a mechanical movement is more than a tool—it’s a statement of appreciation for the heritage of timekeeping.
Quartz Watch Movements
The Precision of Quartz Technology
Quartz movements marked a revolutionary leap forward in the accuracy and affordability of wristwatches. Introduced in the latter half of the 20th century, quartz watches are powered by a small battery that sends an electrical current through a quartz crystal. This causes the crystal to vibrate at a stable frequency—typically 32,768 times per second—which is then used to regulate the watch’s timekeeping functions.
These watches are incredibly accurate and require far less maintenance than mechanical ones. They are also much more affordable, which contributed to their widespread adoption. The typical battery in a quartz watch lasts anywhere from 12 to 24 months. It’s important to replace the battery promptly when it runs out, as a dead battery left inside the watch can leak acid, potentially damaging the movement beyond simple repair.

Atomic
There are also more specialized types of quartz watches that push the boundaries of what these movements can do. One example is the atomic watch. These timepieces are technically quartz watches, but they include a radio-controlled feature that allows them to synchronize automatically with the most accurate clocks in the world—atomic clocks. For wearers in the United States, the signal typically comes from the national atomic clock in Ft. Collins, Colorado. Older atomic watches were limited by time zone compatibility and signal range, but modern versions often feature GPS synchronization, which allows them to adjust to local time no matter where in the world you are.
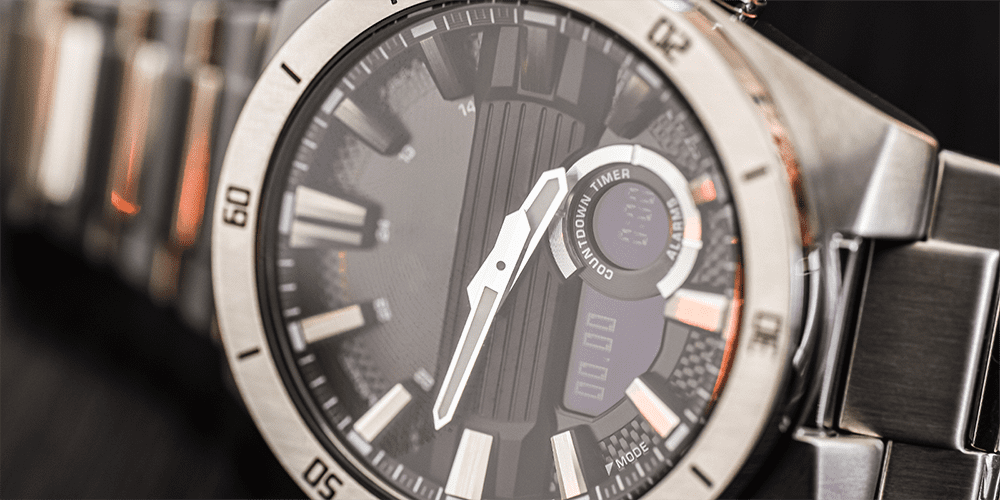

Solar-Powered Watches
Another advancement in quartz movement technology is solar power. In these watches, light—whether natural sunlight or artificial indoor light—is converted into energy, eliminating the need for battery replacements altogether. This makes solar-powered quartz watches a more eco-friendly and convenient option for everyday wear.
Brands Known For Established Quartz Technology
Brands such as Seiko, Timex, and Shinola have established themselves as leaders in quartz technology, while Casio and Citizen are renowned for their atomic and solar-powered offerings.
Connected Watch Movements
The Innovation of Connected Watches
Connected watches, more commonly referred to as smartwatches, represent the most recent evolution in timekeeping. While they don’t fit neatly into the traditional definitions of watch movements, they represent a new kind of “movement”—a shift in how we interact with time and technology on our wrists.
These watches are powered by rechargeable batteries and run operating systems that connect to your smartphone or the internet. They can perform a wide range of functions, from checking text messages and tracking workouts to running apps and receiving GPS signals. In this sense, connected watches are no longer just timepieces—they are compact wearable computers.
Brands Known For Seamless Smartwatch Technology
Though they may lack the mechanical artistry of a traditional watch or the long-lasting dependability of quartz, smartwatches cater to a growing demographic that prioritizes convenience, connectivity, and functionality. Companies such as Apple, Samsung, Fitbit, ASUS, and Pebble have all developed smartwatches that blend style and tech in increasingly seamless ways.
Choosing the Right Watch Movement for You
Selecting a watch often comes down to more than just looks. It’s about how you want your timepiece to function and what role it will play in your life. Mechanical movements offer elegance, history, and craftsmanship—ideal for collectors and those who admire fine engineering. Quartz movements bring unmatched accuracy and simplicity, perfect for those who want reliability without the fuss. Connected watches go far beyond telling time, serving as extensions of your digital lifestyle.
No matter which movement speaks to you, there’s a world of horology waiting to be explored—and appreciated.

Originally Published 10/06/2017, Updated 09/04/2025

Types of Watch Movement Repair & Servicing
Every type of watch movement requires its own kind of care—mechanical watches need regular servicing to keep gears precise, quartz models require timely battery replacements, and even solar or atomic watches benefit from occasional maintenance. Connected smartwatches rely on software updates and battery monitoring, with potential hardware issues over time. For care, maintenance and/or repair of your manual, automatic, standard quartz or atomic watch, visit Watch Movement Repair Services.
The Mechanisms Behind Elite Watch Servicing at My Jewelry Repair
At My Jewelry Repair, our certified watchmakers specialize in servicing and restoring all movement types using state-of-the-art equipment and decades of experience, ensuring your timepiece runs like new—no matter the issue.
Interested in Servicing Your Watch Movement?






Please tell me where I can buy the Bulova Accutron watch you show in your commercial. The watch with the Rams on the bracelet? The commercial at the beginning where Julio is talking and working. My e mail address is (*email removed for privacy*). Thank
Hi Lawrence! Our team has sent you an email with any information we could provide. Have a great day!