
the first ever Wristwatch
Discover the fascinating story behind the first wristwatch ever made—a groundbreaking creation for a queen that forever changed the way we tell time.

The Creation of the First Wristwatch
From Nuremberg Egg to Iconic Timepiece
For something so timeless, the wristwatch had a surprisingly modern beginning. Today, it’s hard to imagine a world without watches wrapped around wrists—but this everyday accessory began as a custom piece of jewelry for royalty. From royal courts to battlefield trenches, the wristwatch evolved from novelty to necessity. Let’s take a look at the very first wristwatch ever created and how it sparked a revolution in timekeeping.
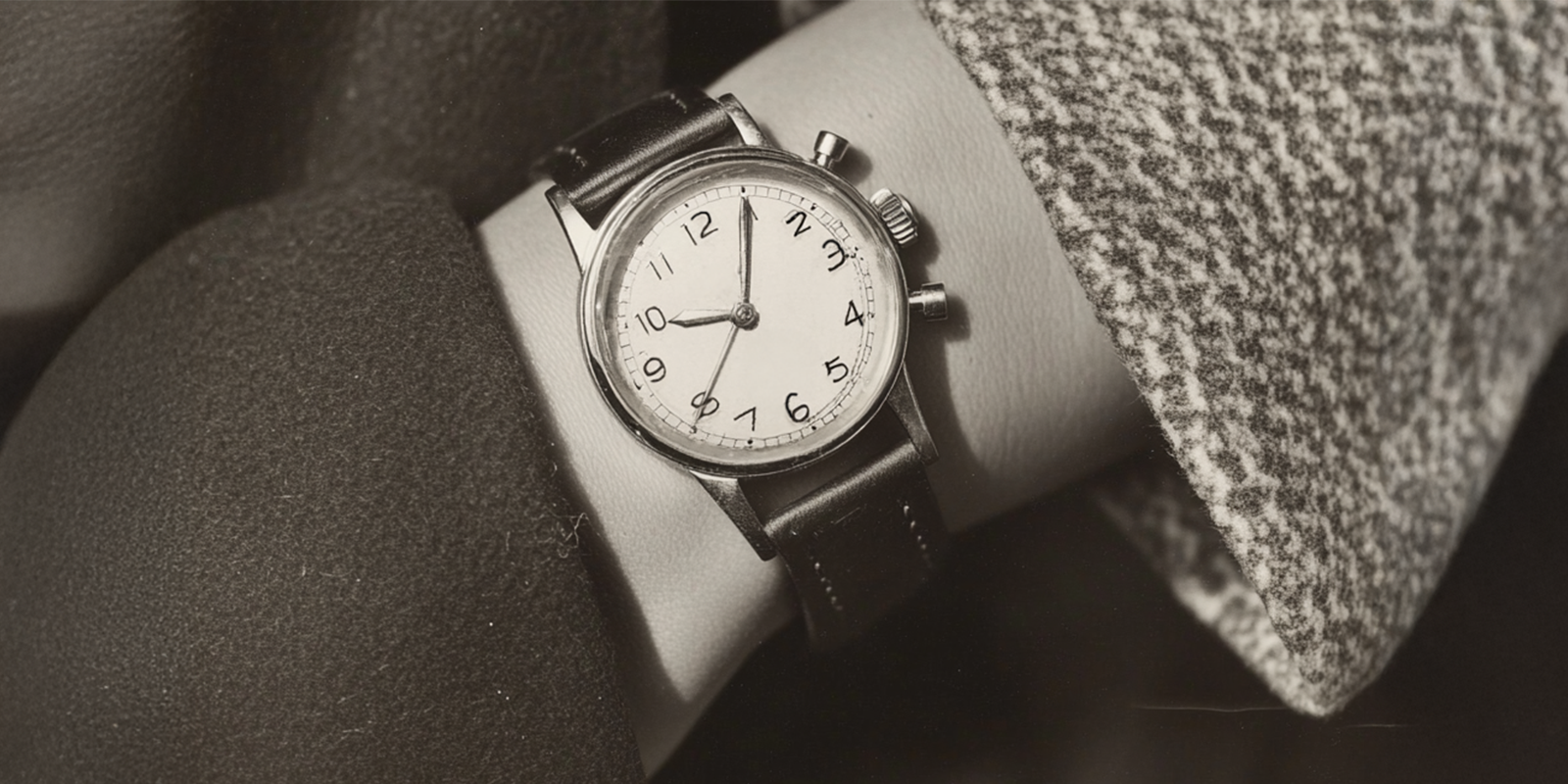

A Royal Commission
The First Wristwatch
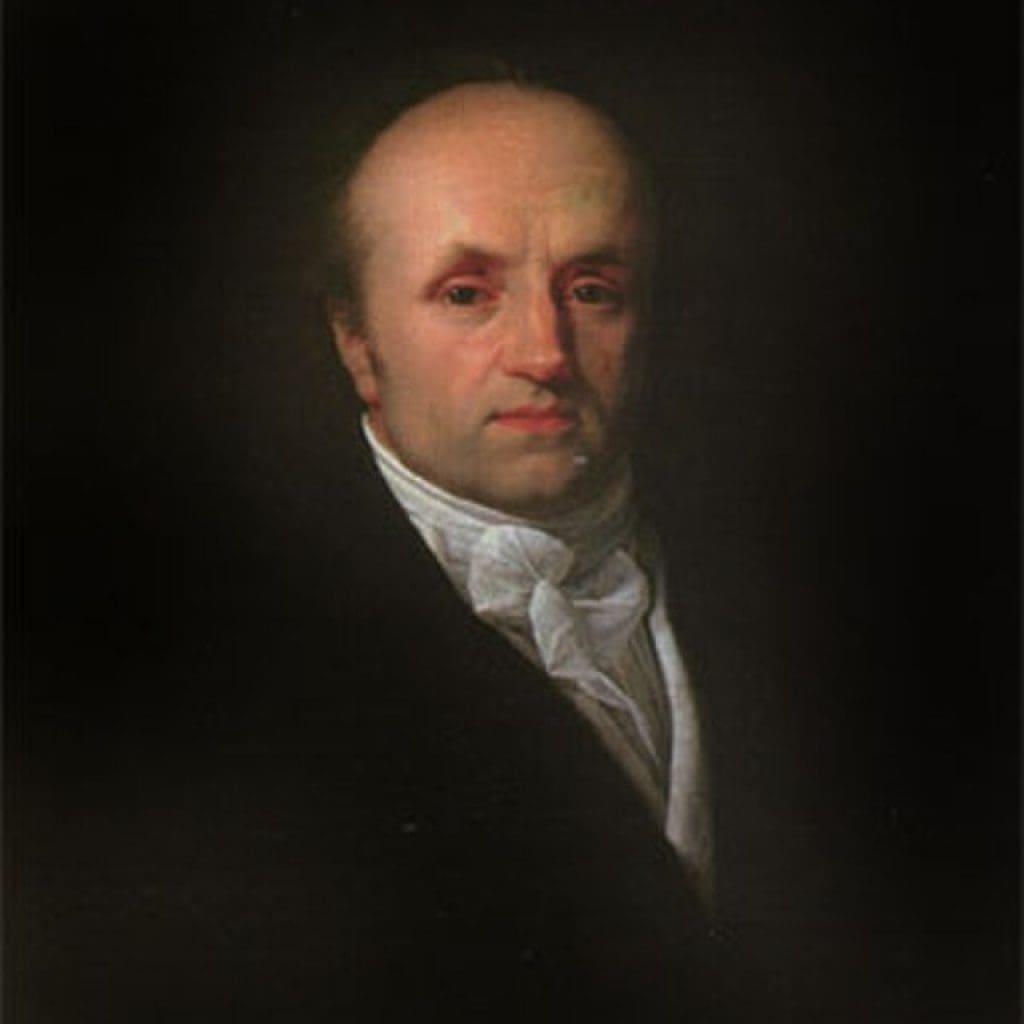
The story of the wristwatch begins in 1812 with Abraham-Louis Breguet, one of the most influential watchmakers in history.
Breguet crafted the world’s first known wristwatch for Caroline Murat, the Queen of Naples and younger sister of Napoleon Bonaparte. She was a woman of refined taste and an avid collector of Breguet’s work, owning over thirty pieces.
This watch was a true original—oval in shape, fitted with a delicate bracelet strap, and designed to be worn on the wrist rather than tucked into a pocket.

At the time, the concept was unheard of. Pocket watches were the standard for men, while women typically wore timepieces on pendants or brooches. But this custom commission set the precedent for a brand new way to carry time.
From Luxury to Legacy
Wristwatches in the 19th Century
Despite its elegance, the wristwatch remained a rarity throughout the 19th century. It was considered more of a decorative bracelet with a clock, rather than a serious timekeeping tool. The idea didn’t catch on widely, especially among men, who viewed wristwatches as too dainty or impractical compared to the robust pocket watch.
However, wristwatches gained popularity among fashionable women in European high society. These early models were often lavishly adorned with gemstones and ornate details, blending form and function. They were seen as luxury accessories rather than tools for precision—which, ironically, is exactly what they would come to represent in the century to follow.
A Wartime Shift
How Wristwatches Went Mainstream
The real turning point came with the outbreak of World War I. Soldiers in the trenches needed quick, hands-free access to time, especially during coordinated attacks. Pocket watches were cumbersome and inconvenient, so many soldiers began strapping them to their wrists using leather bands. Manufacturers took notice, and by the 1910s, watchmakers were mass-producing wristwatches specifically for military use.
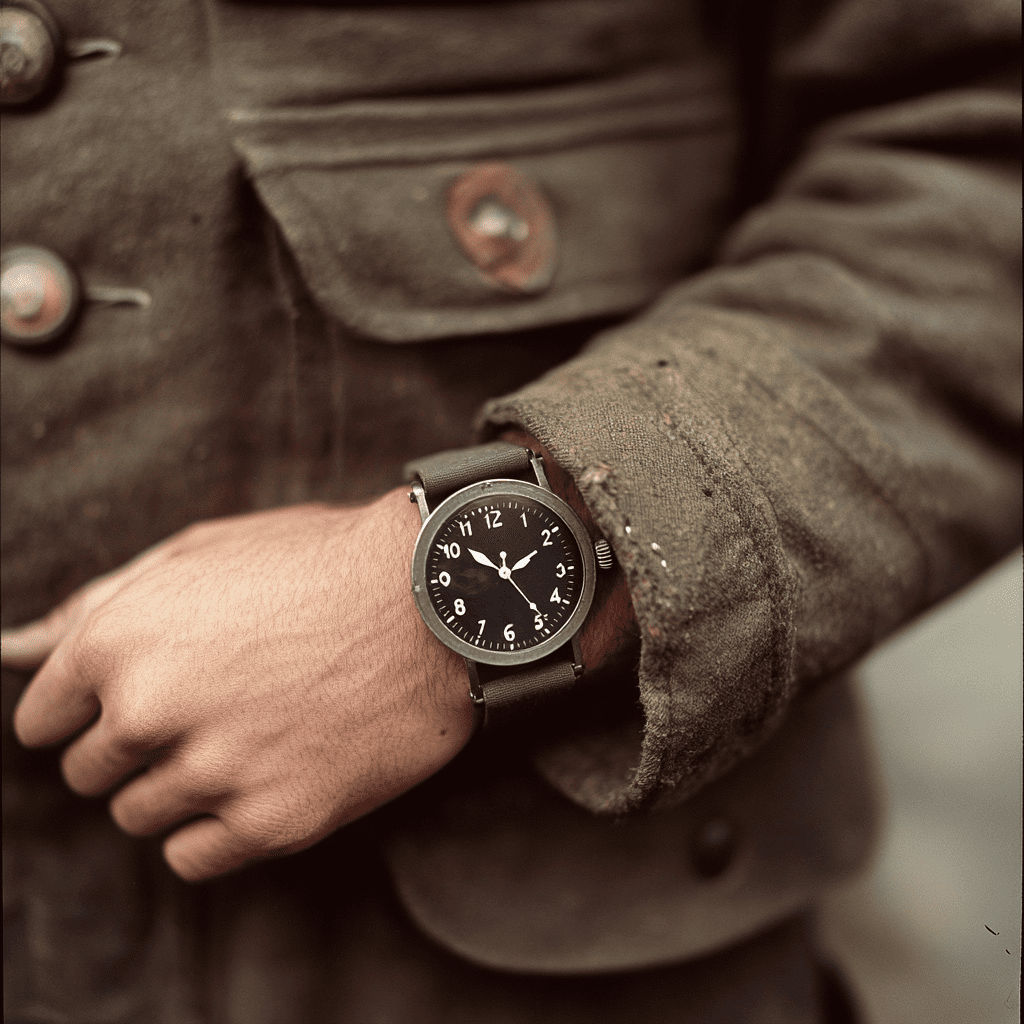

This shift in perception—from feminine ornament to masculine utility—sealed the wristwatch’s place in history. After the war, wristwatches became a symbol of modernity and functionality. Men who had worn them in battle continued to wear them in civilian life, and the trend quickly spread. What began as a royal curiosity had transformed into a global staple.

A Legacy That Keeps Ticking
The wristwatch is more than just a timekeeping tool—it’s a cultural icon. From the elegant Breguet piece made for a queen to rugged field watches worn in war, the wristwatch has always adapted to the needs of its time. Today, it stands at the crossroads of fashion, tradition, and technology.
And it all began with a single, custom-made creation for royalty. The wristwatch may be commonplace now, but its story is anything but ordinary.


Resources:
- The Invention of the Wristwatch: https://www.swisswatchexpo.com/
- When Were Wristwatches Invented? A Timeline of Watch History: https://www.the1916company.com/
- ¹Swiss watchmaker Abraham Louis Breguet from Musée international d’horlogerie, La Chaux-de-Fonds, Photo via Wikimedia: https://commons.wikimedia.org/
- Blog outline and revising assisted by AI resources such as Google Gemini.
Interested in Restoring Your Precious Piece?





Our team has gemologists certified by

We are proud members of the

