
The History of Timepieces
Humankind has been concerned with keeping track of time since we could understand the concept of a future. Before the glamour and intricate machinery of the timepieces we love, we have used temporal queues to understand time.
Ancient civilizations like the Babylonians and Egyptians paved the way, paying close attention to time for the purposes of scheduling shipments, farming, and lunar events. But it is with the Ancient Egyptians that we begin finding devices.

Ancient Timekeeping Devices
Early versions of timekeeping devices were brought to us by the ancient Egyptians, as well as the Greeks and Romans, who used sundials, water clocks, and obelisks to tell time. Sundials and obelisks were shadow clocks. The sun would change relative positions over the course of the day and the sundial was used to show/reflect time changing. Ancient Egyptian obelisks were constructed as early as 3,500 B.C. and are among the earliest shadow clocks in recorded history.
Other early timekeeping devices include water clocks, hourglasses, and candle clocks. From the 1500s onward, hourglass clocks were used to tell time while out at sea. Hourglasses were actually wildly popular due to their dependability, re-usability, and accuracy.

Monastery Clocks and Tower Clocks
When living a monastic life one has to be on time for prayer and daily duties and such. Monasteries used clocks made by medieval clock makers (who also happened to be Christian monks).
Pope Sylvester II built the first known church clock in around 996. Later monks would certainly craft church clocks of higher sophistication, including Peter Lightfoot, who made a clock in the 14th century that is still in use at London’s Science Museum.
In the middle ages, there were many Western European cities that invested in large-scale clock tower construction. Clock towers were used widely and constructed in central locations in order to serve as the community’s primary timepiece.
Pocket Watches
Early watches, which we would call any device that kept time and could be made to be carried or worn by an individual, are believed to have been developed in Italy circa 1500.
In the 1500s the first watches started to appear, the earliest ones made by Peter Henlein, a locksmith from Nürnberg, Germany. Early pocket watches were generally worn around the neck or on a belt and measured hours and not minutes. In 1676, the minute hand was invented by English clock master Daniel Quare.
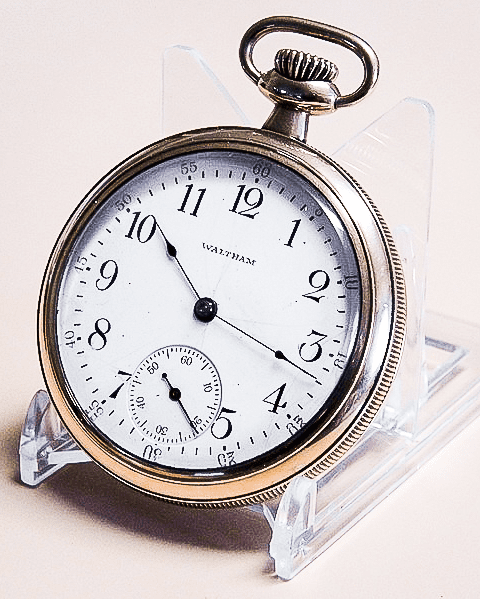

Vintage American Waltham Pocket Watch Model 1908¹
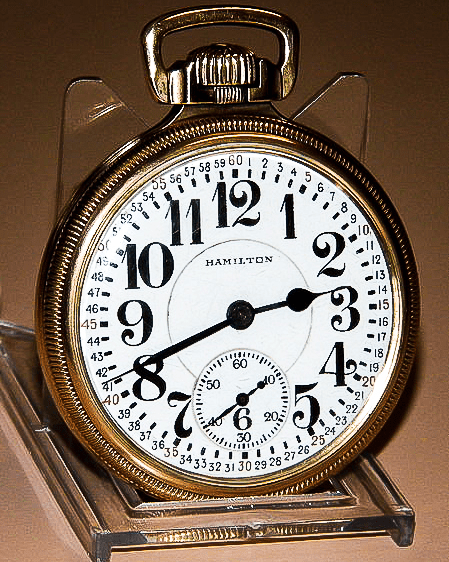
Vintage Hamilton Pocket Watch Railroad Grade Model 1929²
Wristwatches
Henlein also invented the first wearable mechanical timepiece. A prototype to the wristwatch was made by Blaise Pascal (1623-1662) attaching his pocket watch to his wrist with a piece of string in a makeshift fashion.
In 1868 the first actual wristwatch was created by Patek Philippe, a Swiss watch company. The wristwatch was made for Countess Koscowicz of Hungary.
It wasn’t until the turn of the 19th century that watches began to be available to the masses as clocks and watches remained expensive until this time. Less expensive materials begat clock movements from wood. Early watch manufacturers began to craft watches with interchangeable parts as well.

Dive Watches and Water Resistance
Water resistance has been a goal of timekeeping devices since the days of the early clocks, as rust has been an enemy of movements the entire time. Many innovations protecting from dust and moisture had been building on top of each other for centuries.
Many watch manufacturers had been building watches advertised as both “dustproof and waterproof.” Finally in 1926, Hans Wilsdorf and his brother-in-law Alfred Davis, the founders of Rolex in London, created the first truly recognized “waterproof” watch – the Rolex Oyster.

The term “waterproof” is not used for watches today, after the FTC clamped down on these claims amid the understanding that a true waterproof watch is virtually impossible. Today, “Water Resistant” is used instead along with a pressure rating (atmospheres/meters/feet) of water, which gives an idea of just how water resistant the watch is.
Quartz Clocks, Self-Winding Watches, and Beyond
Warren Marrison, a telecommunications engineer developed the first quartz clock in 1927. Marrison was searching for reliable frequency standards and working at Bell Telephone Laboratories at the time. The quartz clock became a highly accurate device based on regular vibrations that the quartz crystal provides within an electrical circuit.
Although the first patent on the self-winding pocket watch was taken out in London in 1780, there was also a patent taken out in 1924 – the self-winding wristwatch by Louis Recordon. This creation featured a swinging weight that was pivoted at the center of the watch movement. This swinging weight was coupled to the barrel arbor via wheels and gears. More modern self-winding watches are fitted with a weight or rotor and swing 360 degrees while winding in both directions.
Electronic watches were first produced in 1953 and became widely used due to their accuracy. Electronic watches operate at an inherently frequency higher than balance-type watches – the tuning fork made a more stable source of frequency.


Resources:
- History Information: https://www.yalescientific.org/
- History Information: https://www.britannica.com/
- History Information: https://www.thoughtco.com/
- History Information: https://www.architecturaldigest.com/
- History Information: https://www.watchmaster.com
- History Information: https://www.hodinkee.com
- History Information: https://www.scientificamerican.com/
- ¹Vintage American Waltham Pocket Watch Model 1908: https://commons.wikimedia.org/
- ²Vintage Hamilton Pocket Watch Railroad Grade Model 1929: https://commons.wikimedia.org/

My Jewelry Repair
Continuing the History of Watches
It doesn’t matter if you’re dealing with a watch of antiquity or something more contemporary, watches require routine care and maintenance to make sure they keep accurate time and stay in good condition. My Jewelry Repair provides an easy online, mail-in service with a long track record of success, performing over half a million repairs each year.
Contact us today to learn more about our easy online jewelry and watch repair service!
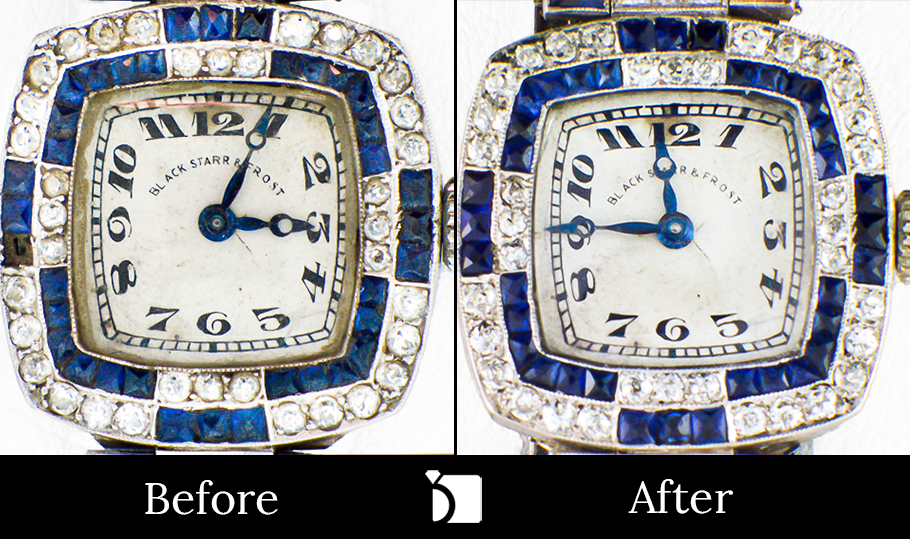

Before & After #35: Vintage 1920’s Black Starr & Frost Timepiece
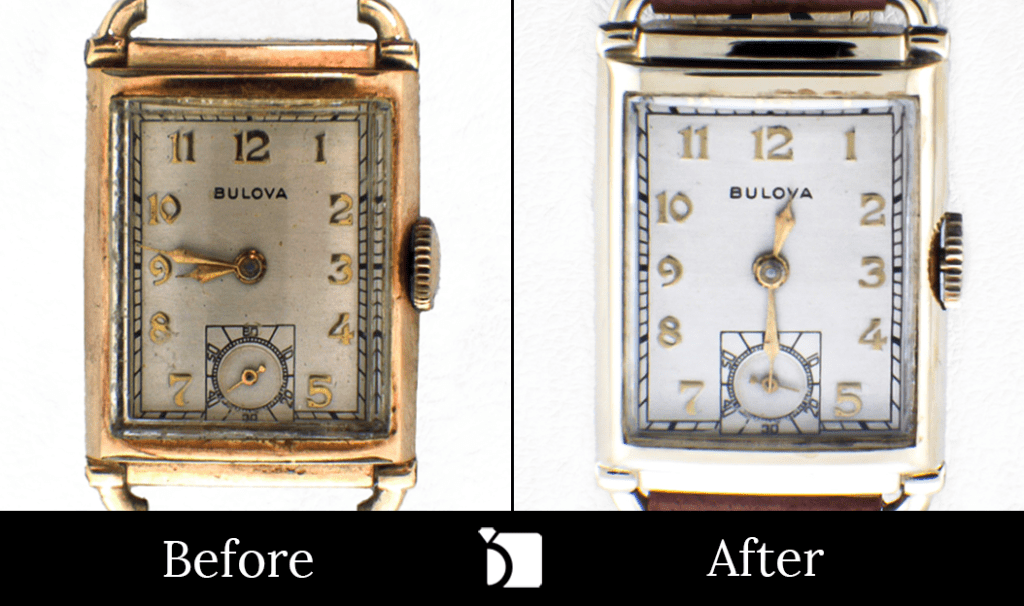
Before & After #28: Vintage 1947 Bulova Timepiece
